yum install
yum remove
yum update
yum search
yum info
yum list
yum list installed
yum provides
yum grouplist
yum groupinstall
yum groupupgrade
yum groupremove
yum repolist
yum repolist all
yum –enablerepo=fedora-source install
yum shell
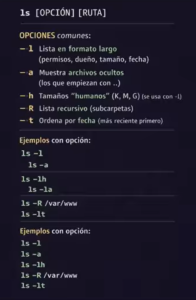
Using Yum from the Command Line
The following table shows some examples of common tasks that you
can perform using yum.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| yum repolist | Lists all enabled repositories. |
| yum list |
Lists all packages that are available in all enabled repositories and all packages that are installed on your system. |
| yum list installed | Lists all packages that are installed on your system. |
| yum list available |
Lists all packages that are available to be installed in all enabled repositories. |
yum searchstring
|
Searches the package descriptions for the specified string. |
yum providesfeature
|
Finds the name of the package to which the specified file or feature belongs. For example: yum provides /etc/sysconfig/atd |
yum infopackage
|
Displays detailed information about a package. For example: yum info bind |
yum installpackage
|
Installs the specified package, including packages on which it depends. For example: yum install ocfs2-tools |
| yum check-update |
Checks whether updates exist for packages that are already installed on your system. |
yum updatepackage
|
Updates the specified package, including packages on which it depends. For example: yum upgrade nfs-utils |
| yum update |
Updates all packages, including packages on which they depend. |
yum removepackage
|
Removes the specified package. For example: yum erase nfs-utils |
yum erasepackage
|
Removes the specified package. This command has the same effect as the yum remove command. |
| yum update |
Updates all packages, including packages on which they depend. |
| yum clean all |
Removes all cached package downloads and cached headers that contain information about remote packages. Running this command can help to clear problems that can result from unfinished transactions or out-of-date headers. |
| yum help | Displays help about yum usage. |
yum helpcommand
|
Displays help about the specified yum command. For example: yum help upgrade |
| yum shell | Runs the yum interactive shell. |
See the yum(8) manual page for more
information.
To list the files in a package, use the
repoquery utility, which is included in the
yum-utils package.
For example, the following
command lists the files that the btrfs-progs
package provides.
# repoquery -l btrfs-progs /sbin/btrfs /sbin/btrfs-convert /sbin/btrfs-debug-tree
yum makes no distinction between installing
and upgrading a kernel package. yum always
installs a new kernel regardless of whether you specify
update or install.
Ver más información en http://www.thegeekstuff.com/2011/08/yum-command-examples/
Más información en https://docs.oracle.com/cd/E37670_01/E37355/html/ol_creating_yum_repo.html